Three-Dimensional Near-Field to Far-Field Transformation for Radar Cross Section Estimation of Elongated Targets via Subdimensional Hybrid Conversion
Article information
Abstract
Image-based (IB) near-field to far-field transformation (NFFFT) is a useful method for the valid prediction of radar cross sections (RCSs) from short-range monostatic measurements. Many previous studies on the IB NFFFT algorithm have been limited to two-dimensional (2D) measurement cases. In this work, a subdimensional hybrid conversion approach is proposed as a relevant three-dimensional (3D) NFFFT method consisting of the following procedures. First, the spherical-wave information collected through 3D scanning is converted to a cylindrical waveform by applying the 2D circular NFFFT (CNFFFT) method to every vertical subplane (r-θ plane). Then, a horizontal far-field radar image on the x-y plane and an RCS pattern are extracted through direct integration of a 2D focusing operator modified to compensate for a magnitude error through distance approximation during the CNFFFT procedure. The results of a comparative study with direct integration of a 3D focusing operator are presented to show the validity and performance of the proposed method.
I. Introduction
The radar cross section (RCS) is a fundamental indicator of stealth during attempts at radar detection, as defined in the far-field (FF) condition. When it comes to performing an RCS measurement, however, FF illumination cannot be implemented easily for several reasons. These include the extremely high cost [1] and the difficulty of securing a long-range test distance [2]. To address these realistic problems, the near-field to far-field transformation (NFFFT) technique has been studied extensively.
Among the various NFFFTs presented to date [3–13], the image-based (IB) technique is highly practical because it can circumvent inconvenient bistatic measurement procedures [3–10]. In most IB techniques [3–6], the quality of the intermediate radar images generated is crucial for accurate RCS prediction.
Thus, to improve the image quality, various imaging processes and techniques have been employed using IB techniques, including fast cyclical convolution [3], non-uniform fast Fourier transform [4], and back-projection methods [5, 6]. Another type of IB technique, circular NFFFT (CNFFFT), which does not actually produce an explicit radar image, has been proposed [7, 8]. Meanwhile, direct integration of the FF conversion operator, known as the focusing operator, has been considered non-implementable due to its huge computational load. In a recent study [9], however, this approach was demonstrated to be a usable solution thanks to the recent advancements in computing capability.
Many of the aforementioned IB technique studies were based on the hypothesis that the target height is short, and two-dimensional (2D) azimuth scanning is thus enough to obtain reliable RCS results [3–9]. Thus, IB technique studies have usually been limited to 2D cases, and few studies have extended to three-dimensional (3D) situations [10]. From a more practical perspective, however, there are numerous cases (e.g., full-scale or tilted aircraft) requiring 3D scanning, thus demanding a relevant 3D NFFFT algorithm.
In this paper, a subdimensional hybrid conversion method is proposed for use as an accurate and efficient 3D NFFFT algorithm. Section II describes the detailed formulation of the sub-dimensional conversion algorithm. In Section III, two near-field (NF) scans (of a truck and an aircraft mock-up) were performed to verify the accuracy and speed of the proposed algorithm. Radar images and RCS patterns converted through the algorithm are presented. These results are also compared with those obtained through the direct integration of a focusing operator.
II. Formulation
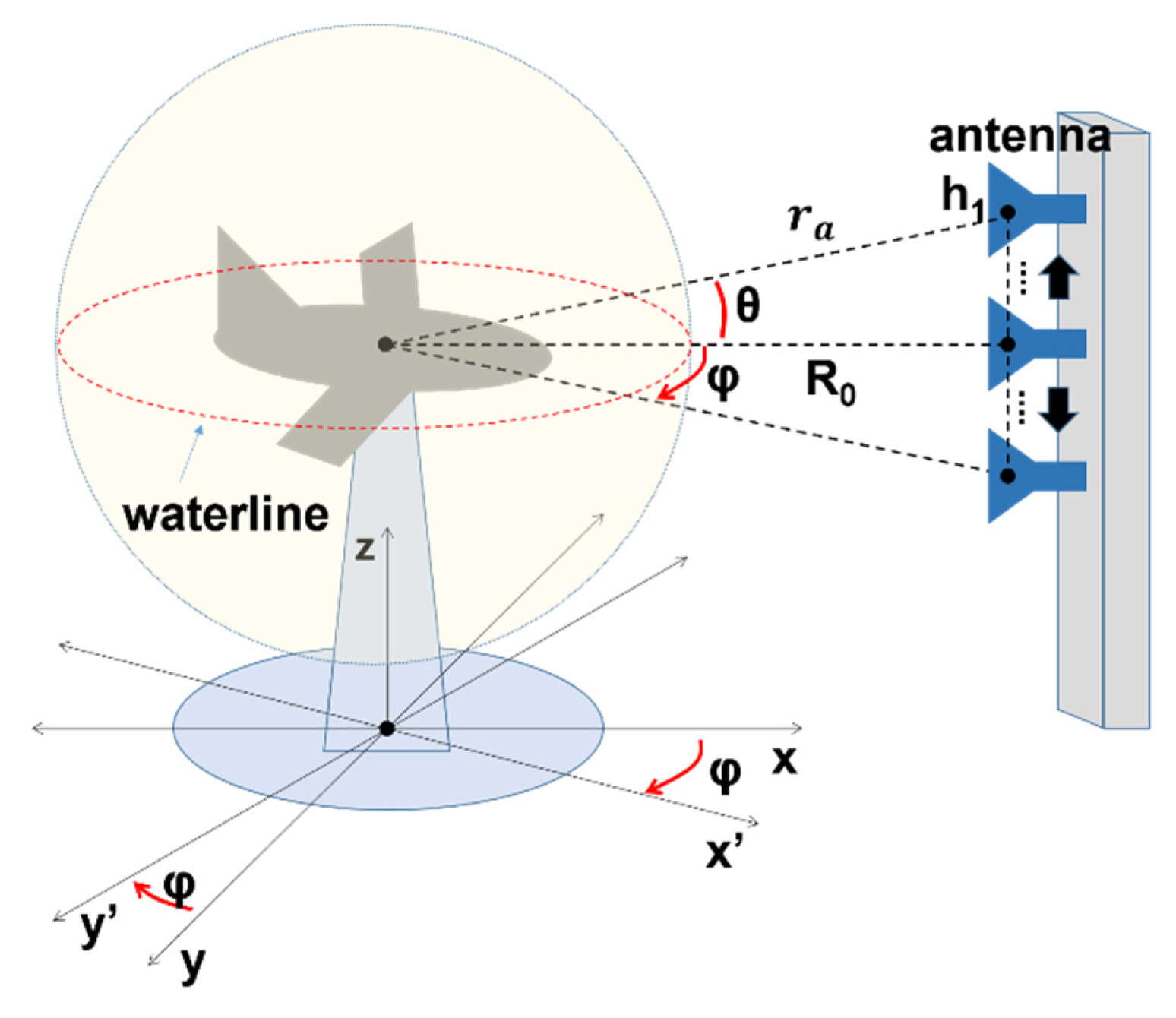
The setup for a 3D scan is illustrated in Fig. 1. A target was positioned on a turntable rotating at angle ϕ, and transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) antennas were moved together along the vertical tower to collect scattering information at different heights (h). The Rx antenna received only co-polarized signals from the Tx antenna. Radio frequency (RF) data were obtained using the stepped-frequency continuous-wave method. Consider the target a set of independent point scatterers where the reflectivity was ρ(r). The backscattered electric field (u) measured by the Rx antenna is given by the following equation:
where ra is the antenna position vector, f is the frequency, k is the wave number, G is the antenna gain, and V is the target volume [7]. In this case, G can be omitted for brevity. ρ(r) is depicted as a pixel in the radar image, and its size is inversely proportional to the scan length [14]. After collecting the backscattered field u, we can evaluate the individual point scatterers using the reverse form of Eq. (1):
where B is the frequency bandwidth [4, 6, 7, 9]. Here, the kernel function (
where rϕ is the antenna position vector when θ = 0. The target scattering pattern S and RCS are then calculated using a set of scattering points ρ(r):
where r̂ is the directional vector of antenna (ra) and σ is the RCS.
According to Sensani et al. [9], direct integration of a focusing operator is more accurate than any other fast-Fourier-transform-based imaging process technique. However, for 3D cases, this operation requires an enormous computational load, which causes too much time delay (Fig. 2(a)).
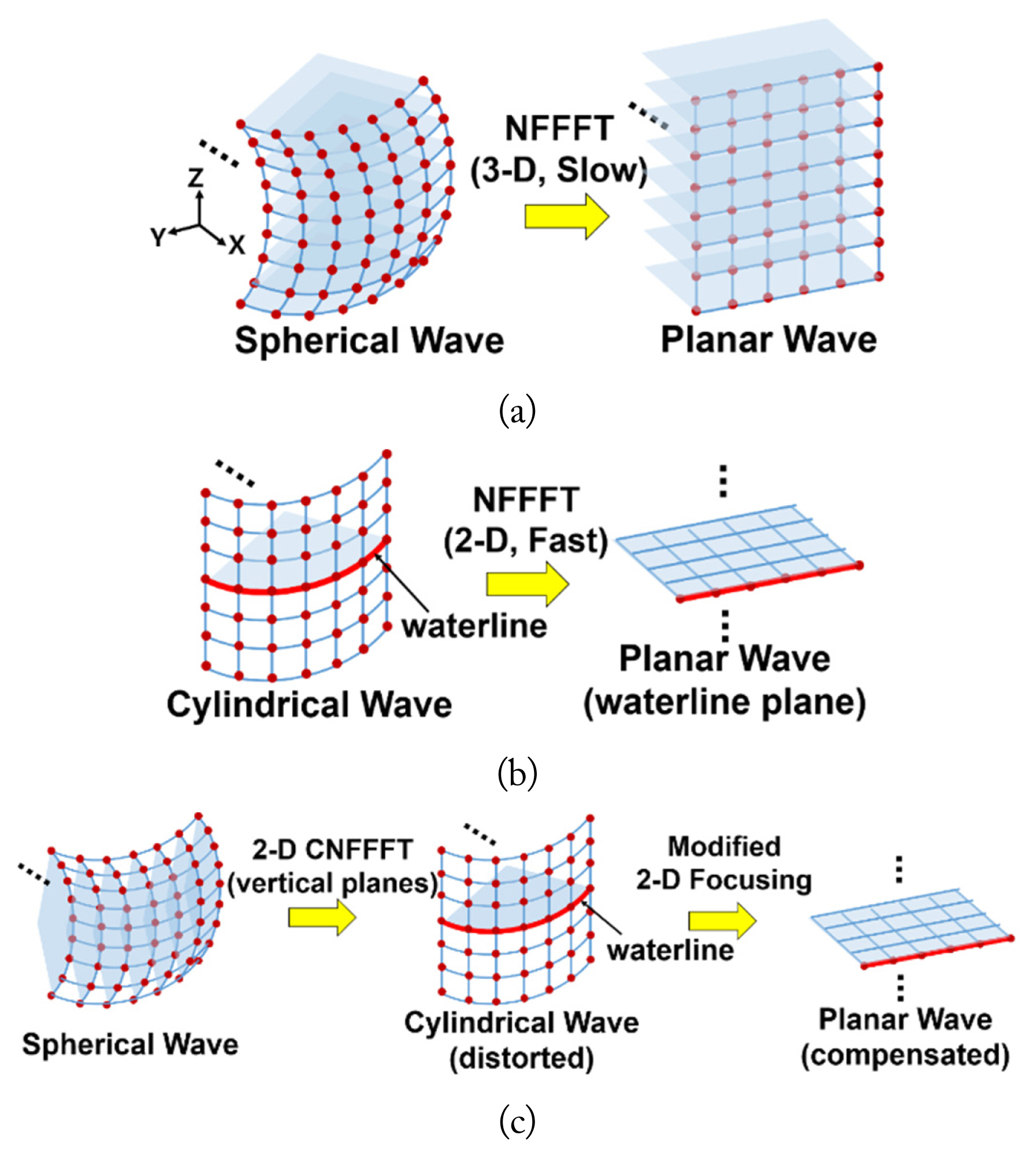
Conceptual illustration of (a) a general three-dimensional (3D) near-field to far-field transformation (NFFFT), (b) a two-dimensional NFFFT, and (c) the 3D subdimensional conversion algorithm proposed in this work.
We should note that the 2D operation is valid only if the received field satisfies the FF criterion in the vertical direction (i.e., a cylindrical waveform), as shown in Fig. 2(b). To satisfy this condition, the first step of the subdimensional conversion is to alter the collected spherical waveform to form a cylindrical one using the CNFFFT method. In other words, every r-θ subplane is converted to the r-z subplane, expressed as follows:
where M is the total number of r-z subplanes, Scyl is the converted cylindrical scattering pattern for a single r-z subplane,
Specifically, the aforementioned error becomes more severe as the ratio of the target dimension to the measurement distance increases. However, we resolved this error by adding the term
where the term
III. Results and Discussion
First, we measured the NF of a truck sample with the dimensions 3.8 m (L) × 1.5 m (W) × 2.0 m (H) (Fig. 3(a)). The measurement distance was 20 m. The central frequency was 3.2 GHz, with a 2 GHz bandwidth (2.2–4.2 GHz, with 1,051 samples), and the azimuth angle was from −17.5° to 17.5°, with 121 samples. The center height of the Tx and Rx antennas was 4 m, and the vertical scan length was 6 m, with 0.1 m steps. The tripod was covered with radar-absorbing material. We applied subdimensional conversion to extrapolate the FF radar image and RCS pattern. For comparison, we also used direct integration of a focusing operator (focusing operation).
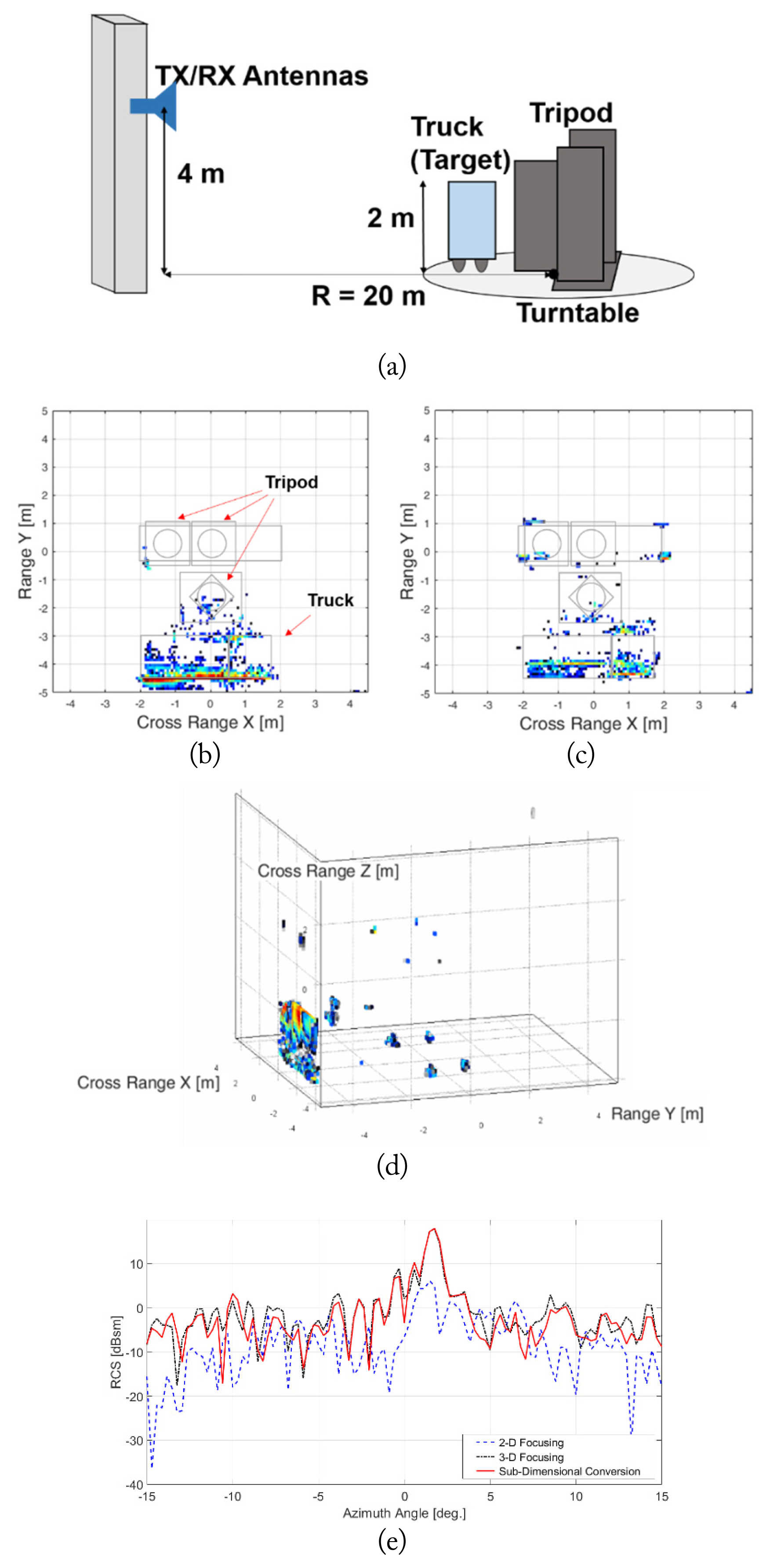
(a) Simplified illustration of near-field measurement of a truck for radar cross section (RCS) extraction. (b) Two-dimensional (2D) image constructed through sub-dimensional conversion (antenna height of 4 m). (c) 2D radar image constructed through direct integration of a 2D focusing operator with a 2D scan. (d) Three-dimensional (3D) image constructed through direct integration of a 3D focusing operator. (e) RCS of the truck over the azimuth angle extracted through near-field to far-field transformation.
Fig. 3 shows a set of constructed radar images of the truck sample. The major component contributing to the backscattered field was the side surface of the truck, which was equivalent to a rectangular metallic plate. At this 20 m range, the backscattered field in the vertical direction could not meet the standard FF criterion.
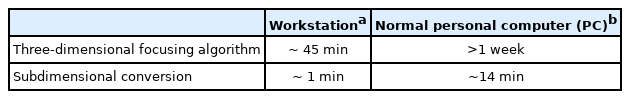
where R, D, and λ are the measurement distance, target dimension, and wavelength, respectively. Thus, a 2D focusing operation with a 2D scan at the antenna center height was insufficient to create a reliable FF radar image (Fig. 3(c)). Accordingly, the RCS peak attributed to the normal reflection from the side surface does not appear in Fig. 3(e) (blue-dotted line). On the other hand, very intense reflection from this surface was observed in the image constructed through subdimensional conversion (Fig. 3(b)). This is because the NF received in the vertical direction was converted to FF by CNFFFT. This surface was also clearly constructed in a 3D image generated by the 3D focusing operation (Fig. 3(d)). The resulting RCS patterns were almost identical in both cases. However, as shown in Table 1, the processing speed for the subdimensional conversion was much faster than that for the 3D focusing operation. The 3D focusing algorithm and subdimensional conversion can also be compared in terms of analytical complexity. The complexity of Eq. (2) is O(lmn), but the complexity of Eq. (9) is O(n)+O(lm), where l is the number of frequency samples, m is the number of azimuth angle samples, and n is the number of vertical samples. In Eq. (9), regardless of r and ϕ, it is first computed for θ in Eq. (6).
Furthermore, subdimensional conversion enabled us to reduce the vertical scan length without sacrificing accuracy. According to Eq. (11), cross-range resolution and vertical scan length are directly related to each other.
where ρCR–V is the vertical cross-range resolution, λ is the wavelength, R0 is the distance of the target from the antenna, and L is the vertical scan length [9]. In particular, for low-frequency or long-range measurements, it is hard to secure a fine vertical cross-range resolution (ρCR–V) due to the physical restriction of long-range vertical scanning. Thus, low-quality radar images are created, which are not appropriate for the accurate extraction of an RCS. However, with the subdimensional conversion method, the CNFFFT method converts to the FF in the vertical direction. Because CNFFFT does not produce an intermediate-constructed radar image and does not convert to FF from an explicit radar image, the size of ρCR–V is of no concern for the extraction of an accurate RCS. This advantage allows for the shortening of the vertical scanning length and time.
The aforementioned speculation was demonstrated using an NF scan of the aircraft model with the dimensions 10.5 m (L) × 7 m (W) × 2.3 m (H) (Fig. 4(a)). Here, the measurement distance was 200 m, and the frequency was 3.2 GHz, with a 2 GHz bandwidth (2.2–4.2 GHz, with 1,401 samples). The horizontal and vertical edges were aligned in the azimuth direction, and the azimuth scan angle included this direction. The vertical scan range was 9 m, with 0.3 m steps. The vertical height of the aircraft model was 2.3 m, and, according to Eq. (10), the minimum length needed to guarantee that FF will be in the vertical direction is ~112 m, which is even shorter than our measured distance (200 m). Therefore, as references, a 2D FF radar image and an RCS pattern were extracted using a 2D focusing operation with 2D scanning.
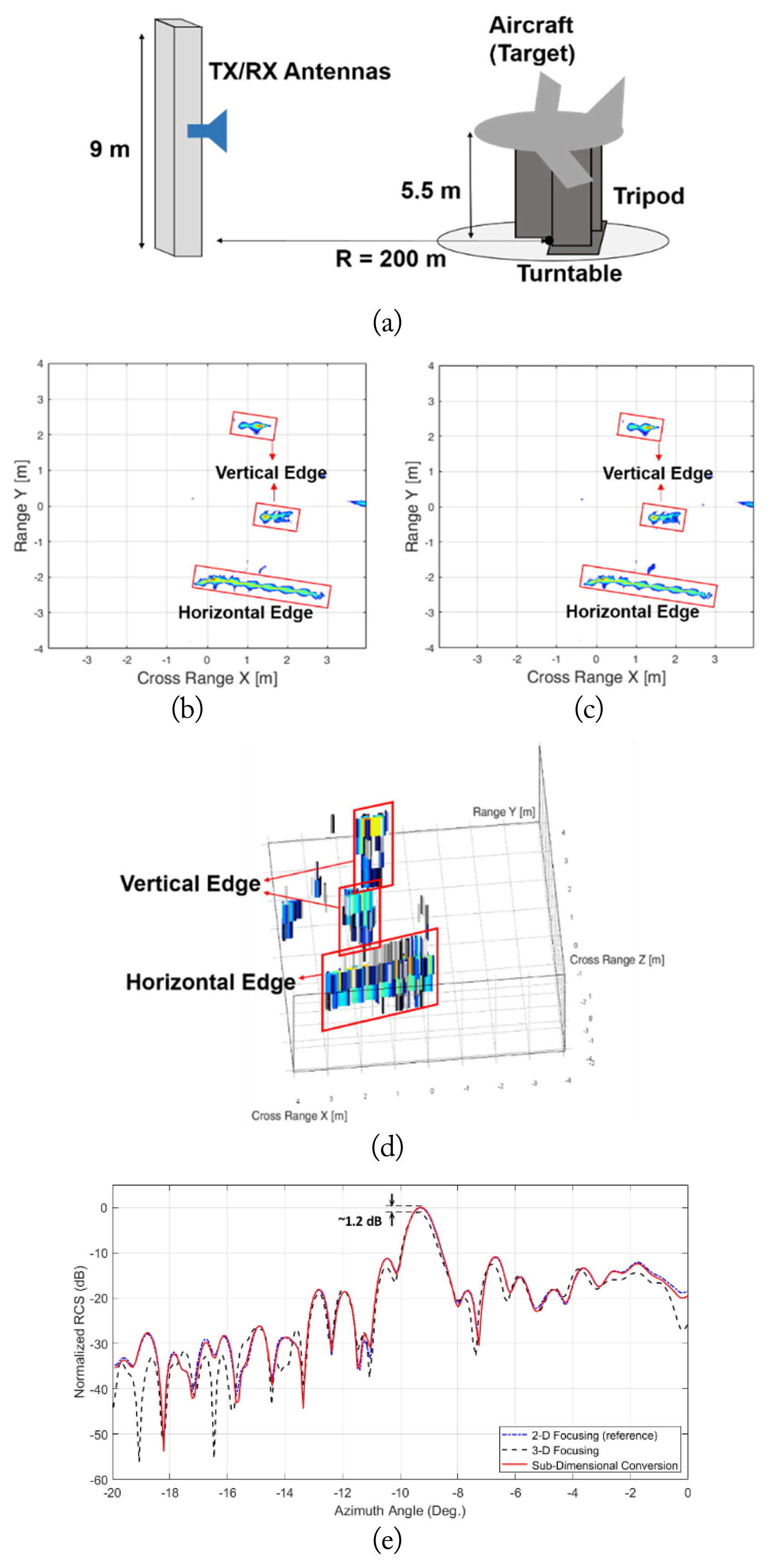
(a) Simplified illustration of the near-field measurement of an aircraft mock-up for radar cross section (RCS) extraction. (b) Filtered two-dimensional (2D) image constructed through subdimensional conversion. (c) Filtered 2D image constructed through direct integration of a 2D focusing operator with a 2D scan. (d) Three-dimensional (3D) filtered radar image constructed through direct integration of a 3D focusing operator. (e) RCS of the aircraft over the azimuth angle extracted through near-field to far-field transformation.
Fig. 4(d) shows a filtered 3D radar image of the aircraft mock-up created using a 3D focusing operation. Except for the horizontal and vertical edges, all the other scattering points were filtered by the image-gating function. Because ρCR–V was too large (~1.04 m), the image quality was severely degraded in the vertical direction; point scatterers composed of the horizontal and vertical edges were spread by an over 3 m length in the vertical direction. Hence, the distorted image resulted in an inaccurate RCS pattern (black-dotted line in Fig. 4(e)) that deviated from that extracted by the 2D focusing operation (reference, blue-dotted line in Fig. 4(e)). This result suggests that a longer vertical scan is needed to obtain more accurate RCS patterns when a 3D focusing operation is used. In contrast, a 2D image constructed through subdimensional conversion (Fig. 4(b)) is almost identical to that constructed by the 2D focusing operation (Fig. 4(c)). Therefore, excellent concurrence is identified in the RCS patterns in Fig. 4(e) (red line vs. blue-dotted line), indicating that the 9 m vertical scan length is sufficient for extracting accurate images and RCS patterns. We expect that the vertical scan length can still be further reduced without compromising the determined accuracy level of the RCS.
IV. Conclusion
In this paper, a subdimensional hybrid conversion method is proposed as a relevant 3D IB NFFFT algorithm. It has shown better efficiency in RCS extraction than direct integration of a 3D focusing operator. Moreover, unlike with other IB NFFFT techniques, we found that its conversion accuracy was maintained even if the vertical scan length was relatively short. This will be very useful for reducing the total scanning time.
References
Biography

Jeong-Kyu Kim received B.S. and M.S. degrees in electrical engineering from Korea University in Seoul, Korea, in 2013 and 2015, respectively. From 2015 to 2021, he worked on NFFFT algorithm development at the Agency for Defense Development (ADD) in Seosan, Korea. He is currently a Ph.D. student in the Department of Electrical Engineering at Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA.

Hyun-Sung Tae received a B.S. degree in electronics and materials physics from Osaka University in Osaka, Japan in 2011 and M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in Daejeon, Korea in 2014. In 2014, he joined ADD in Korea. He is currently a senior researcher at ADD in Daejeon, Korea. His research interests are RCS measurements and defense test and evaluation research.

Min-Gyeong Seo received B.S. and M.S. degrees in radiowave engineering from Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea in 2011 and 2013, respectively. She is currently a senior researcher at ADD in Seosan, Korea. Her research interests include RCS measurement and NFFFT.

Ho-Min Park received B.S. and M.S. degrees in electrical engineering from KAIST in Daejeon, Korea, in 2015 and 2017, respectively. In 2017, he joined ADD in Seosan, Korea. He is currently a researcher at ADD in Seosan, Korea. His research interests are NFFFT and NF RCS measurements.